Introduction
Social skills play a crucial role in a child’s development, encompassing elements such as play, conversation, emotional understanding, and problem-solving. These social skills in autistic children not only contribute to healthy relationships but also impact a child’s overall mental health and quality of life. In this article, we explore the significance of social skills in autistic children, with a focus on strategies to help children, particularly those with autism, develop and apply these skills effectively.
The Importance of Social Skills for Children
Social skills, including play, conversation, emotional management, and problem-solving, are fundamental for children’s interaction in various social settings. They equip children with the tools to communicate with grandparents, engage with friends at school, and navigate familial relationships. Beyond immediate social interactions, these skills lay the foundation for building friendships, learning from others, developing hobbies, and fostering a sense of belonging.
Strategies for Developing Social Skills in Autistic Children
Practice Play
Utilizing play as a learning tool is highly effective in developing social skills. Parents can engage in play activities that involve turn-taking, coping with winning and losing, and following rules. Simple games or role-playing with toys can create scenarios for children to practice essential skills in a relaxed setting.

Unlocking the vibrant spectrum of connection: In the tapestry of social skills, autistic children weave a unique thread, creating a mosaic of understanding and empathy that transcends conventional boundaries.
Ellen Notbohm
Praise
Positive reinforcement is key to reinforcing desired behavior. Providing ample praise and encouragement when an autistic child exhibits positive social interactions, such as sharing or taking turns, can significantly enhance their social development. Acknowledging and praising specific actions help reinforce these behaviors.

Role-Play
Before social events or playdates, engaging in role-play with autistic children can prepare them for potential scenarios. This includes suggesting games, practicing shared activities, and discussing topics for conversation. For older children, introducing social problems in role-playing, such as sharing limited resources, helps develop problem-solving skills.

Social Skills Training
Structured social skills training programs, such as the Westmead Feelings Program or the Program for the Education and Enrichment of Relational Skills, can be beneficial for autistic children. These programs, offered in individual or group therapy sessions, focus on teaching emotions and social skills in a systematic way.

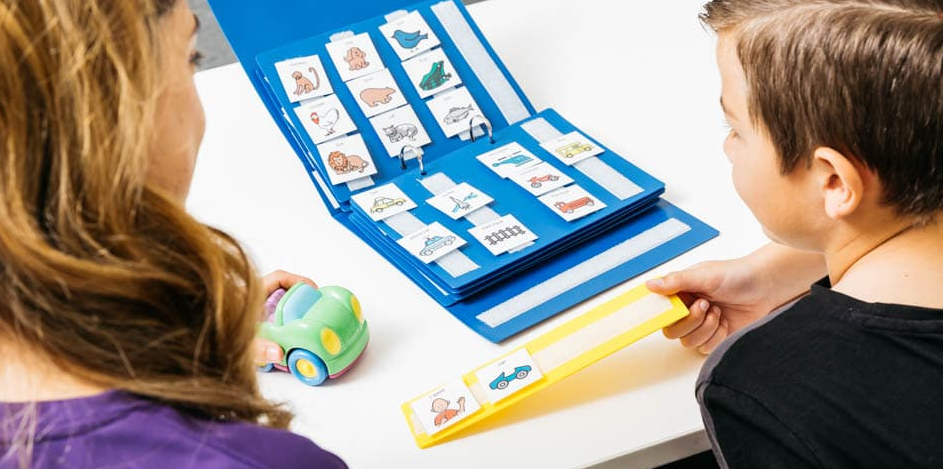
Visual Supports
Visual aids, including pictures, words, checklists, or prompt cards, can assist autistic children in learning and remembering social skills. Customizing visual supports based on the child’s learning needs helps reinforce specific behaviors. For instance, using pictures to prompt conversation topics or guide through game sequences.

Applying Social Skills in Different Settings
Autistic children may face challenges in transferring learned social skills across different settings. To address this, consistent communication between parents and teachers is essential. Aligning prompts used at home and school ensures continuity. Additionally, practicing social skills in diverse situations, such as sharing with friends during visits or at a café, enhances a child’s ability to generalize these skills.
Conclusion
Cultivating social skills in children, especially those with autism, demands patience, consistency, and personalized strategies. By incorporating play, positive reinforcement, role-playing, structured training programs, and visual supports, parents can empower their children to navigate social interactions successfully, fostering meaningful connections and a sense of well-being.